The Future of CNC Machining: Precision, Innovation, and Efficiency
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining has revolutionized the manufacturing industry, providing businesses with the ability to produce parts and components with unmatched precision and efficiency. From aerospace to automotive, healthcare to electronics, CNC machining has become a cornerstone of modern manufacturing. In this blog post, we’ll explore the current trends, technological advancements, and future directions of the CNC machining industry
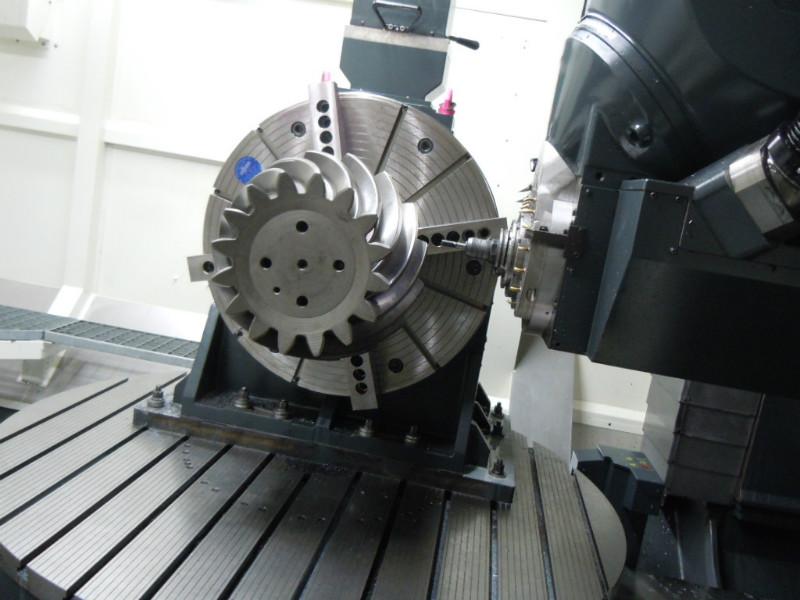

What is CNC Machining?
CNC machining involves using computer-controlled machines to cut, shape, and mill materials such as metals, plastics, and composites. These machines follow programmed instructions, allowing for high precision and repeatability. Unlike traditional manual machining, where the operator controls the machine directly, CNC machining allows for automated, error-free, and faster production processes.
This ability to automate intricate processes with such precision has made CNC machining the preferred choice in many sectors, including aerospace, automotive, medical, and electronics.
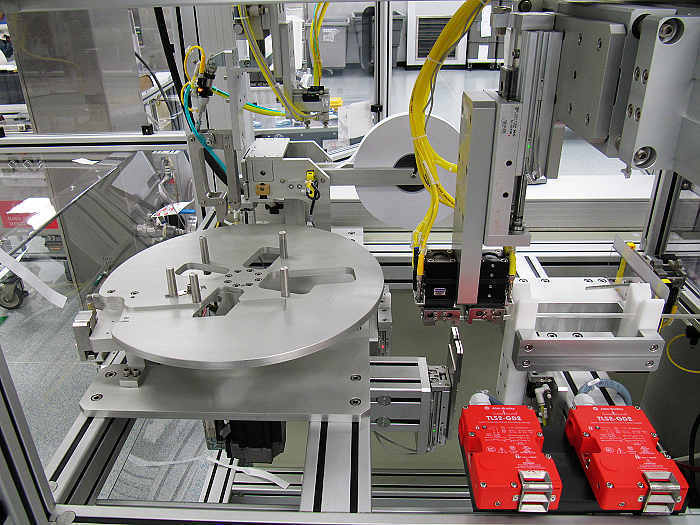
Why Is CNC Machining So Important?
There are several key reasons why CNC machining is crucial for modern manufacturing:
1. Unmatched Precision: CNC machines can produce parts with an incredible level of accuracy, often down to the micron level. This high precision is especially critical in industries where even the smallest defect can result in catastrophic failure, such as aerospace and medical device manufacturing.
2. Increased Production Efficiency: Once a CNC machine is programmed, it can operate continuously with minimal human intervention, leading to faster production cycles. This reduces lead times and allows businesses to meet the growing demand for quick turnarounds and high-volume production runs.
3. Flexibility in Design: CNC machining is highly versatile. It can produce a wide range of shapes, sizes, and complexities, from simple parts to complex geometries that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional methods. This flexibility allows manufacturers to explore innovative designs without worrying about constraints in manufacturing capabilities.
4. Consistency and Reproducibility: One of the standout advantages of CNC machining is its ability to replicate exact results with each part produced. Whether it's producing a single prototype or thousands of identical components, CNC machines ensure that every piece is made to the same standard, eliminating human error and variation in production.
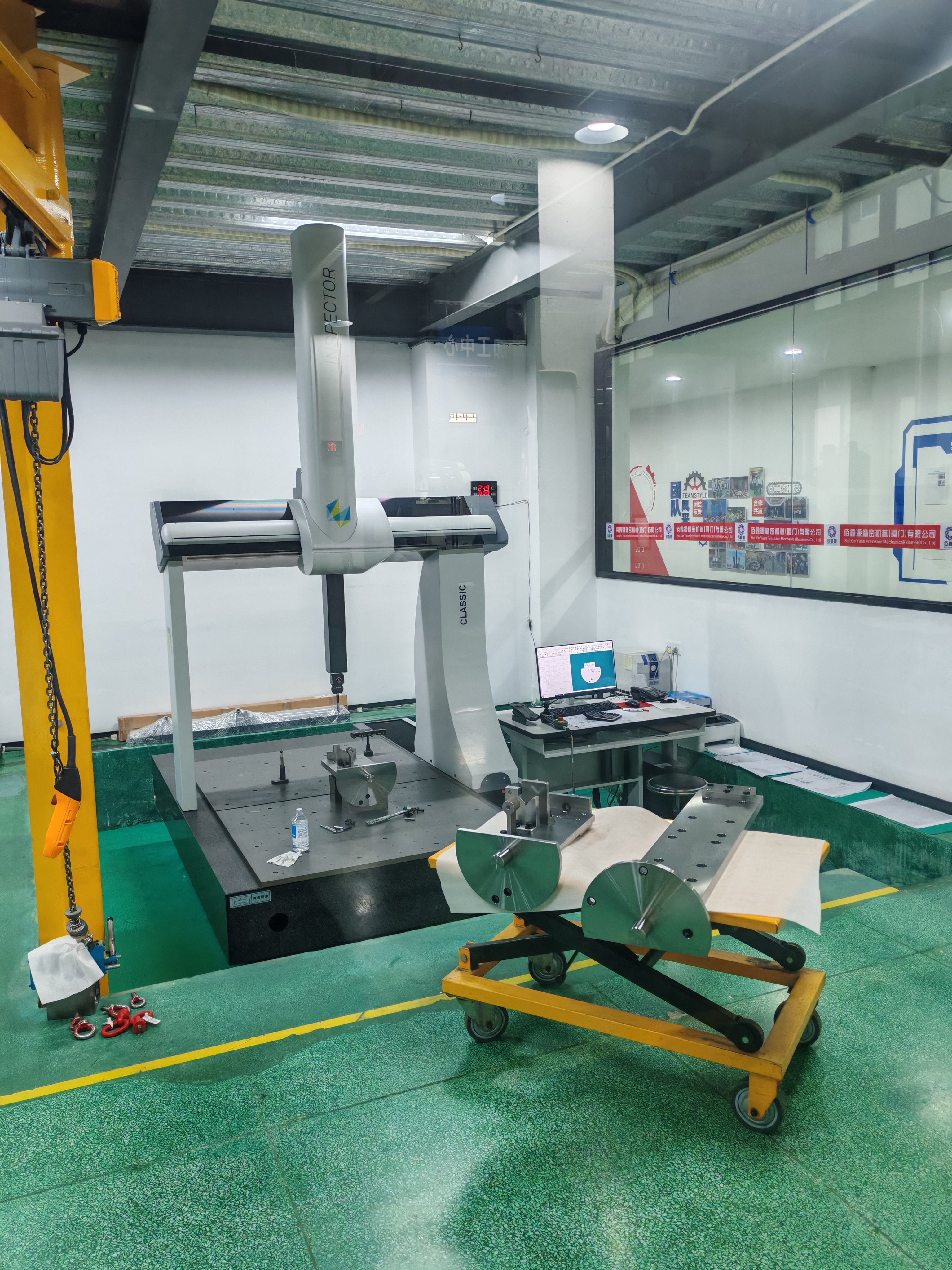

Technological Advancements Shaping CNC Machining
The CNC machining industry is not standing still; it's evolving rapidly with the integration of advanced technologies. These developments promise to push the boundaries of what’s possible in manufacturing.
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI and machine learning are increasingly integrated into CNC machining. AI enables real-time performance monitoring, predictive maintenance, and process optimization. By analyzing data from the machine, AI can adjust parameters to improve the machining process, reducing downtime and improving production efficiency.
2. Internet of Things (IoT): IoT allows CNC machines to connect and communicate with other machines and devices, creating an interconnected manufacturing environment. By leveraging IoT technology, manufacturers can monitor machine health, track production in real-time, and optimize workflow efficiency from anywhere in the world.
3. Hybrid Manufacturing (CNC + 3D Printing): As 3D printing technology advances, its integration with CNC machining opens up new possibilities. Hybrid manufacturing combines additive (3D printing) and subtractive (CNC machining) methods to produce complex parts with intricate details and superior material properties.
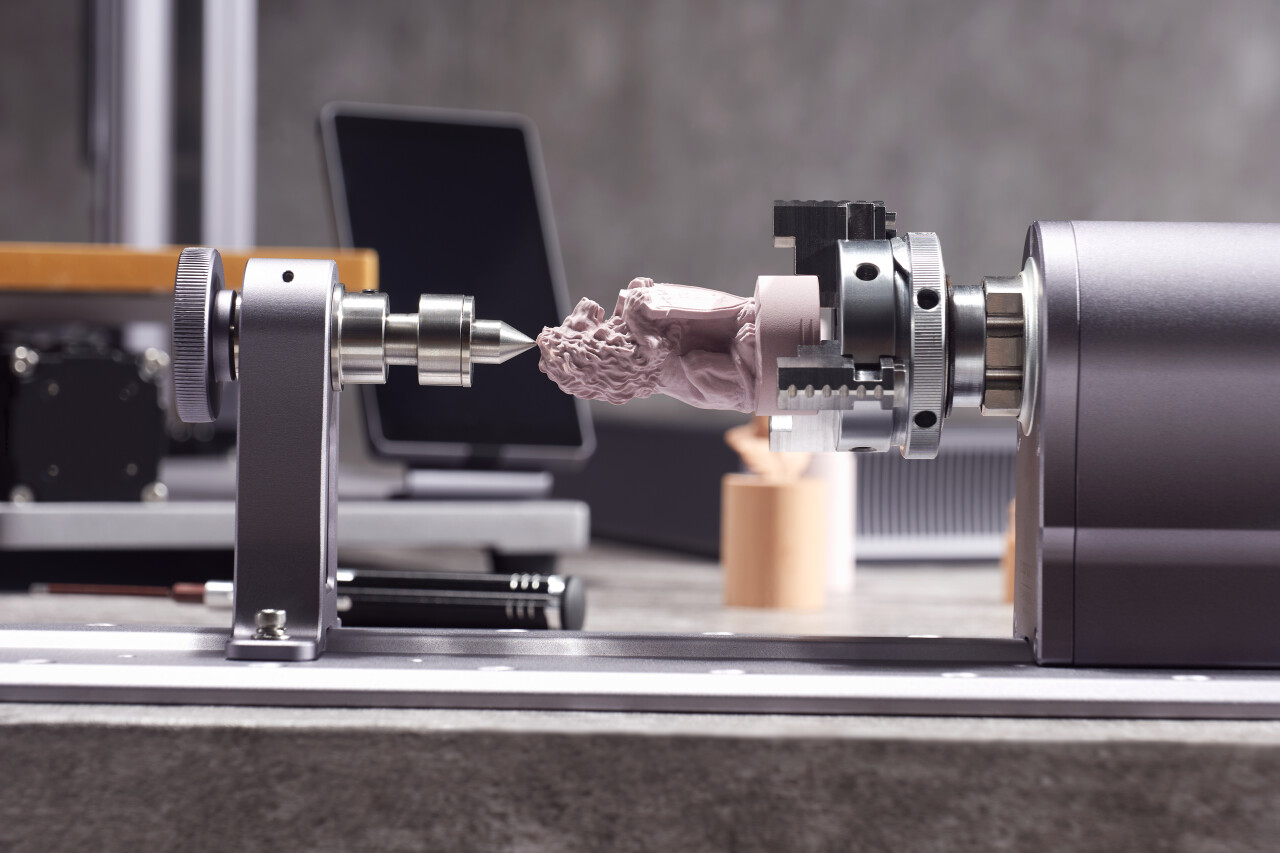
CNC Machining in Different Industries
CNC machining is used across a wide variety of industries, each benefiting from its unique capabilities:
1. Aerospace: The aerospace industry requires parts that meet extremely high standards of performance and reliability. CNC machining enables the production of complex and high-precision components like turbine blades, engine parts, and structural components.
2. Automotive: In the automotive industry, CNC machining is used to produce components such as engine blocks, transmission parts, and specialized tools. With the rise of electric and autonomous vehicles, CNC machining will play a critical role in manufacturing components for these new technologies.
3. Medical Devices: CNC machining is essential in the production of medical implants, surgical instruments, and prosthetics, where precision is vital for patient safety and product effectiveness. Customization options in CNC machining also enable manufacturers to create patient-specific solutions.
4. Electronics: As electronic devices continue to become more compact and intricate, CNC machining is increasingly used to produce small, complex parts such as housings, connectors, and circuit boards, ensuring that every component fits together perfectly.
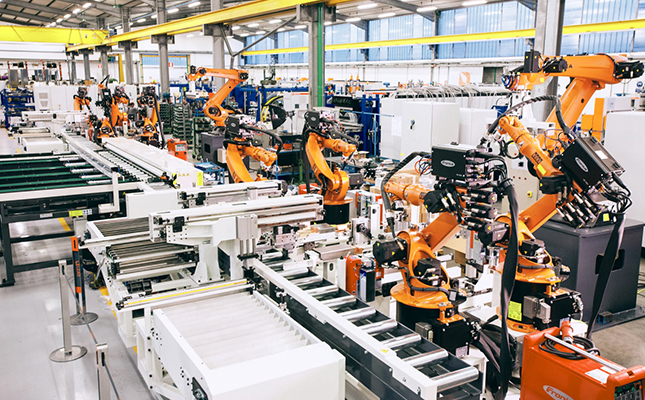

Looking Ahead: The Future of CNC Machining
The future of CNC machining holds immense potential. As Industry 4.0 progresses, the integration of smart manufacturing technologies will become the norm. CNC machines will become even more connected, intelligent, and automated, allowing manufacturers to streamline operations, reduce costs, and enhance production quality.
Moreover, with growing concerns about sustainability and resource efficiency, CNC machining will continue to evolve to minimize waste and energy consumption. New technologies are being developed to make CNC machines more eco-friendly, further reinforcing the industry's ability to lead in both innovation and environmental responsibility.